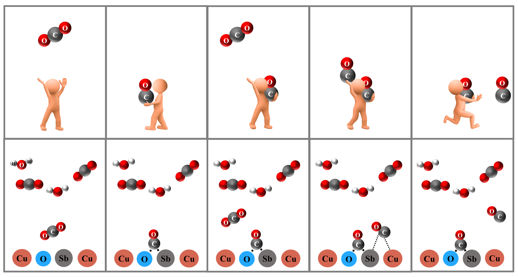
近日,课题组博士生陈红宇的论文“Facile synthesis of antimony-doped Cu/Cu2O catalyst with robust CO production in broad potentials for CO2 electrochemical reduction”被Journal of Materials Chemistry A (2021年中科院SCI期刊一区TOP期刊,IF=12.732)接收!该工作研究了新型antimony-doped Cu/Cu2O复合材料在电催化还原CO2中的高性能催化行为,包括高选择性单一产物、宽催化电势、高能量效率,在流动池中展现了极高的催化活性,并通过DFT计算和实验验证详细揭示了催化剂高活性的起源,这项工作将为高选择性CO2还原催化剂的研究提供新的思路,并为高选择性CO2还原催化剂的设计铺平道路。
Electrocatalytic CO2 reduction reaction (CO2RR) on copper-based catalysts is a promising method to produce valuable chemicals, but its selectivity is much lower than expected largely due to insufficient research on the structure of new materials. Herein, antimony-doped Cu/Cu2O (Cu/Cu2O-Sb) catalyst is developed for highly selective CO2RR to CO. The synthesized Cu/Cu2O-Sb exhibits intensive suppression to hydrogen evolution, low overpotential and high Faradaic efficiency (FE) towards CO. The CO selectivity is as high as ~95% with a partial current density of ~6.3 mA cm-2 at -0.9 V and maintains over 90% in a broad range of potentials. DFT calculations reveal that the doping of antimony achieves the distinct activation of CO2 and suppression of hydrogen evolution. Meanwhile, the pre-adsorbed *CO significantly promotes the desorption of the neighboring *CO, which is the key for high selectivity of CO2 to CO. This work will provide a new consideration for the origin of high selectivity during CO2RR and pave the way toward design of highly selective CO2 reduction catalysts.
https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2021/ta/d1ta06181j