近日,课题组硕士生尚益竹论文“Toward Highly Active Electrochemical CO2 Reduction to C2H4 by Copper Hydroxyphosphate”被Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry接收!
Abstract:
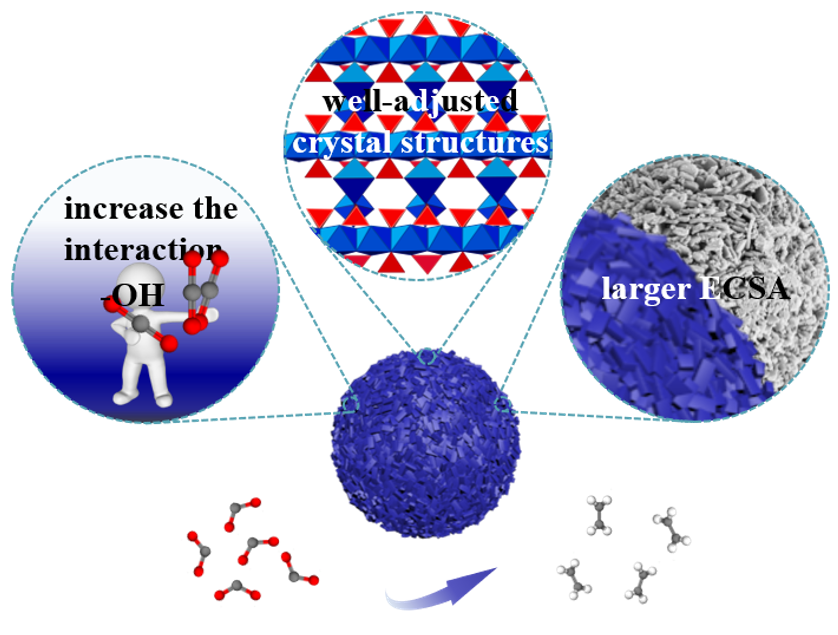
Electrocatalytic carbon dioxide reduction reaction (CO2RR) is a promising method to deal with the greenhouse effect and the energy crisis. In a well-designed Cu-based catalyst, the unique crystal structure with active electronic properties is crucial for CO2RR. Here, a series of copper hydroxyphosphate catalysts were synthesized via one-step solvothermal process and applied in CO2RR. The concentration of hydroxide ion (OH-) and ammonium ion (NH4+) plays an important role in the formation and aggregation of the crystal architectures. Compared to copper monohydroxyphosphate (Cu2(OH)PO4), copper tetrahydroxyphosphate (Cu5(OH)4(PO4)2) exhibits superior selectivity and activity for CO2RR to C2H4. The Faradaic efficiency of C2H4 was achieved over 37.4% with the outstanding stability. The unique structure and morphology characteristics endow Cu5(OH)4(PO4)2 with more hydroxyl groups (-OH) and higher catalytic area. It affords the high CO2RR performance by not only increasing the interaction between the catalysts and CO2 molecules, but also providing more active sites for CO2RR. This work provides a new perspective for the design of stable novel Cu-based catalysts with tunable chemical environment for CO2RR.