近日,课题组硕士生刘庆龙论文“Post-modification of UiO-66-NH2 enhances the interfacial interaction of mixed matrix membranes for Efficient CO2/N2 separation”被ACS Applied Polymer Materials(2023中科院SCI二区, IF=4.4)
Abstract
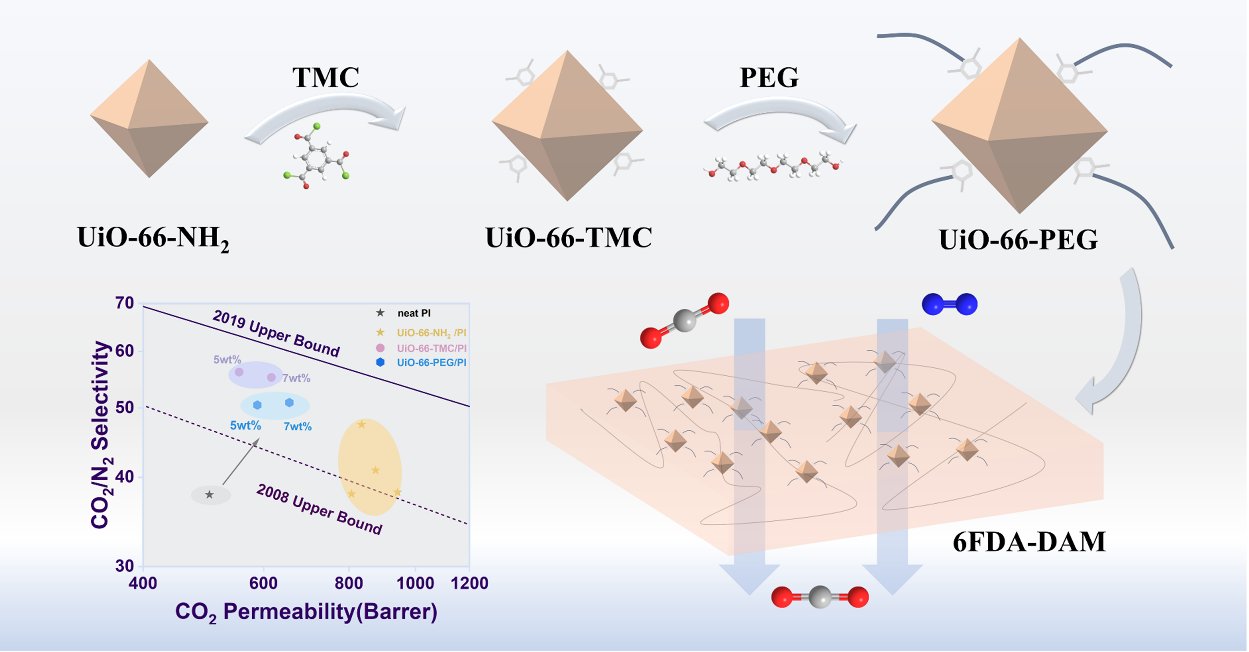
MOFs-filled mixed matrix membranes have great potential to overcome the trade-off effects of traditional gas separation membranes. However, achieving good interfacial compatibility and adequate dispersion of MOF is not straightforward. Several studies have confirmed the improvement in gas separation performance of MMMs by optimizing the interface between a polymer matrix and inorganic filler, e.g. UiO-66 functionalized with -NH2 group. However, they still have limitations of decreasing the active surface area or a multistep operation process which is different from case to case and less of universality. In this study, we introduce flexible polymer chains through the covalent grafting method. UiO-66-NH2 was easily modified with Trimesoyl chloride (UiO-66-TMC) and polyethylene glycol (UiO-66-PEG), which was utilized as fillers to construct Polyimide (PI) based mixed matrix membranes (MMMs). The rich interactions between modified UiO-66-NH2 and the PI matrix contribute to the efficient CO2/N2 separation. At 25°C and 0.1 MPa, UiO-66-TMC/PI MMMs exhibited a CO2/N2 selectivity of 55.3, and a CO2 permeability of 616.17 Barrer, and those are 56.7 and 686 Barrer for UiO-66-PEG200/PI MMMs. Both of them exceed the 2008 Robeson upper bound. The ether bonds in PEG exhibit strong interactions with CO2 molecules and improve CO2 dissolution selectivity. Meanwhile, the introduction of organic ingredients realized good dispersion and interfacial compatibility within the PI matrix.This work lays the groundwork for further fabricating highly selective CO2 separation materials with specific microscopic interface structures and properties.